LAB 6 Pelvic Limb
Pelvic Limb Osteology
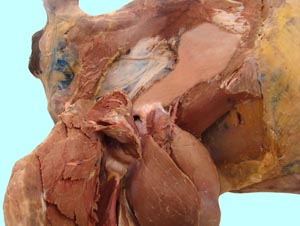
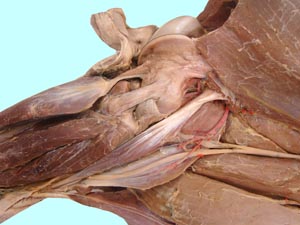
Hip, Thigh, Stifle and Crural Dissection
Lab Objectives:
• To study the osteology of the upper pelvic limb.
• To dissect the hip and thigh region.
• To dissect the stifle region.
• To expose the cranial lateral crural muscles.
• To expose the caudal medial crural muscles.
Anatomical Terms:
Osteology and Associated Structures
femur
femoral trochlea
medial ridge
lateral ridge
extensor fossa
supracondylar fossa
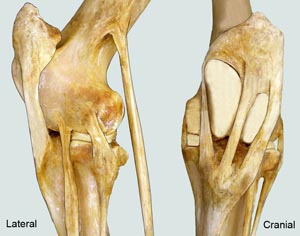
tibia
tibial tuberosity
extensor groove
medial malleolus
lateral malleolus
Pelvic Limb Muscles and Associated Structures
tensor fasciae latae m.
fascia lata
quadriceps femoris m.
rectus femoris m.
vastus lateralis m.
vastus medialis m.
gracilis m.
adductor m.
sartorius m.
pectineus m.
femoral a.
inguinal lymph nodes
iliopsoas mm.
prepubic tendon
patellar ligaments
medial
middle
lateral
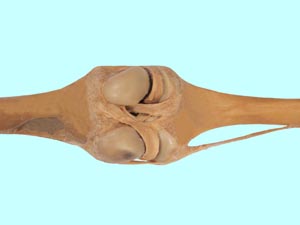
collateral ligaments of the stifle joint
medial
lateral
cranial cruciate ligament
caudal cruciate ligament
long digital extensor m.
fibularis (peroneus) tertius m.
cranial tibial m.
lateral digital extensor m.
gastrocnemius m.
superficial digital flexor m.
tibial n.
medial & lateral plantar nn.
deep digital flexor m.
lateral head
medial head
Instructor Commentary:
The term reciprocal apparatus refers to a pair of tendons that cause the tarsal joint to flex and extend when similar action occurs in the stifle joint so that tarsal motion mimics (reciprocates) the action of the stifle joint. Stifle motion is caused by active muscle contraction but the resultant tarsal motion is a passive propagation of stifle movement. The reciprocal tendons are the fibularis tertius which causes tarsal flexion and the superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) which causes tarsal extension.
The hind limb stay apparatus consists of three parts: (1) the stifle locking mechanism, (2) the caudal part of the reciprocal apparatus, and (3) the suspensory apparatus which is similar to that of the forelimb. The stifle joint is locked by a ligamentous loop that gets caught on a hook like protrusion of the distal femur. Ungulates have 3 patella ligaments. The ligamentous loop is formed by the patella and its medial and middle ligaments. Once the stifle joint is locked the SDFT part of the reciprocal apparatus locks the tarsus as well. Therefore, the reciprocal apparatus not only causes reciprocal motion of the tarsus, but also reciprocal locking. Note that the SDFT causes digital flexion but it also causes extension of the tarsus.
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 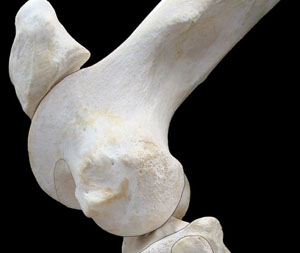 |
 |
2 |
| 3 |  |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 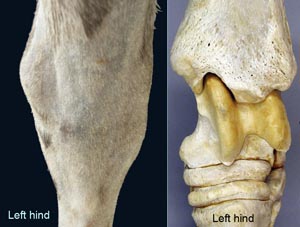 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 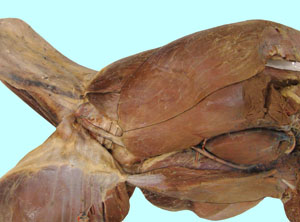 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 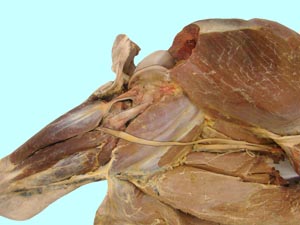 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 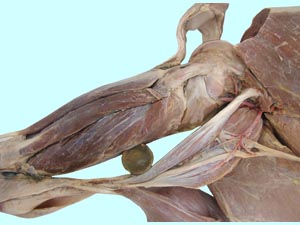 |
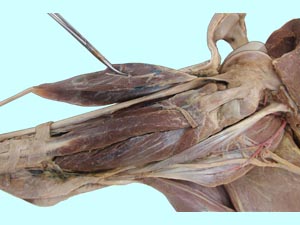 |
12 |
| 13 | 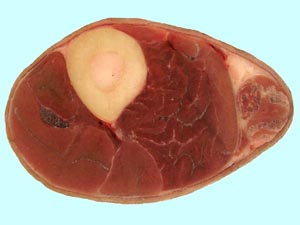 |
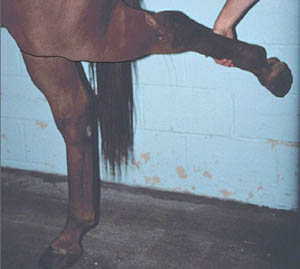 |
14 |
| 15 |  |
 |
16 |
