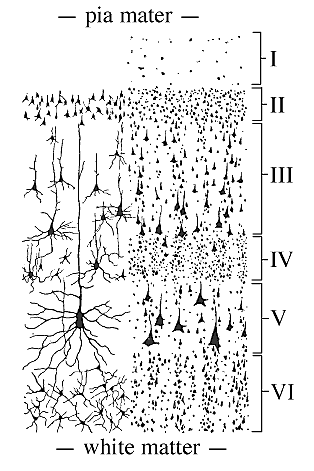
Cerebral cortex is gray matter covering the cerebral hemisphere. Cortex outside of the rhinencephalon, so-called neocortex, has six horizontal layers.
The labeled image illustrates the six cortical layers. On the left side, Golgi silver precipitation of selective neurons is shown. The right side shows a Nissl stain.
Pyramidal cells (neurons) and granular cells predominate in the cerebral cortex (layer 6 has multiform cells). Pyramidal cells send axons into the underlying gray matter. Granular cells are interneurons that remain within the cortex.
The six layers are:
I = molecular layer
II = outer granular layer
III = outer pyramidal layer
IV = inner granular layer
V = inner pyramidal layer
VI = multiform layer
The outer layers receive non-specific afferents which serve to keep the cortex awake. Layer IV receives specific afferents, which bring the specific information that activates the particular cortical cell column.