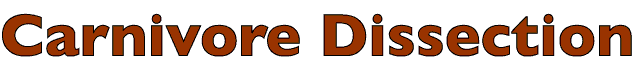
LAB 17 Introduction
Abdominal Viscera & Nerves
Peritoneal Structures
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 166-174)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Examine abdominal viscera:
- pancreas (pancreatic lobes, pancreatic ducts, and duodenal papillae)
- adrenal glands
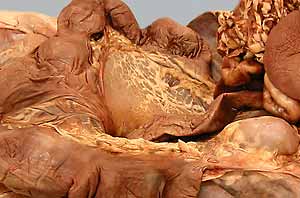
- kidneys (renal hilus; renal cortex and medulla)
-- ureter (renal pelvis & pelvic recesses)
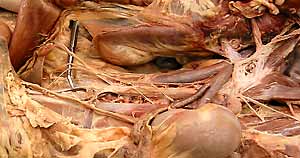
• Examine female internal genitalia:
- ovary ( and proper ligament of ovary)
- uterine tube (and infundibulum)
- broad ligament of the uterus (connecting peritoneum):
mesovarium & suspensory ligament of ovary
mesosalpinx & ovarian bursa
mesometrium & round ligament of the uterus
• Identify "mesenteries" of the alimentary tract:
- greater and lesser omentum and omental bursa
- mesoduodenum
- mesentery (mesojejunum, mesoileum, & root of mesentery)
- mesocolon
- mesorectum
also, liver ligaments (falciform ligament, coronary, & triangular)
• Identify autonomic nerves and sympathetic ganglia:
- vagus nerve, vagal branches and vagal nerve trunks
- sympathetic trunk and splanchnic nerves
- celiac plexus and cranial mesenteric plexus (celiacomesenteric plexus)
-- celiac ganglia & cranial mesenteric ganglion
- caudal mesenteric plexus & ganglion
- right/left hypogastric nerves
Anatomical Terms:
Abdominal viscera - (continued)
pancreas (left lobe, body, & right lobe)
pancreatic duct
accessory pancreatic duct
major and minor duodenal papillae
adrenal glands (right & left)
kidneys (right & left [palpate] )
hilus
renal cortex
renal medulla
pyramids
renal crest
arcuate branches (of renal vessels)
renal sinus
ureter
renal pelvis
pelvic recesses
ovary
proper ligament of the ovary
uterine tube
infundibulum
abdominal ostium (not easily seen)
tuberouterine junction
uterus (cervix, body, uterine horns)
broad ligament of the uterus
mesovarium
suspensory ligament of the ovary
mesosalpinx
ovarian bursa
mesometrium
round ligament of the uterus
Peritoneum
parietal & visceral peritoneum
connecting peritoneum:
lesser omentum
hepatoduodenal ligament
greater omentum
omental bursa
epiploic foramen
mesoduodenum
duodenocolic fold
mesentery (mesojejunoileum)
root of the mesentery
mesocolon
(ascending, transverse, descending)
ligaments of the liver:
right triangular ligament
left triangular ligament
coronary ligament
falciform ligament
umbilical vein remnant (round ligament of the liver)
Abdominal viscera: nerves
vagus nerve (right & left )
dorsal & ventral branches
dorsal & ventral vagal trunks
branch to celiacomesenteric plexus (celiac br.)
sympathetic trunk (right & left )
major splanchnic n.
minor splanchnic n.
lumbar splanchnic nerves
celiacomesenteric plexus & ganglia:
celiac plexus
right & left celiac ganglia
cranial mesenteric plexus
cranial mesenteric ganglion
caudal mesenteric plexus & ganglion
right & left hypogastric nerves
Note:
omentum [Latin] = fatty skin
epiploic [Greek: epiploon] = omentum
peritoneum [Latin] from per = around & teinien = to stretch
falciform [Latin] from falx = sickle and forma = form
Instructor Commentary:
The major duodenal papilla, which receives both the bile duct and the pancreatic duct, is always present cranially in the duodenum. The minor duodenal papilla, which receives the accessory pancreatic duct, is generally present in the dog but present in only a minority (20%) of cats. The minor papilla is absent when the accessory pancreatic duct has atrophied.
The suspensory ligament of the ovary tethers the ovary to the dorsal abdominal wall. During a spay operation (ovariohysterectomy), the suspensory ligament must be manually disrupted in order to bring the ovary to the incision site where ovarian vessels are accessible for ligation.
The evolutionary value of an extensive greater omentum probably relates to limiting peritonitis. The peritoneal cavity offers invading bacteria a good location to reproduce and to spread throughout the abdomen. An infection (abscess) that results from puncture through the abdominal wall or through the gut wall would tend to spread throughout the abdomen unless it is encapsulated. The encapsulation process is greatly facilitated by adhesion of greater omentum to the inflamed surface, bringing leukocytes and fibroblasts to an otherwise exposed surface.
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
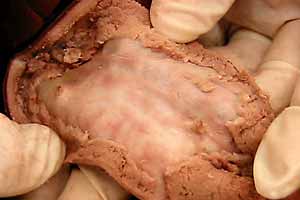
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 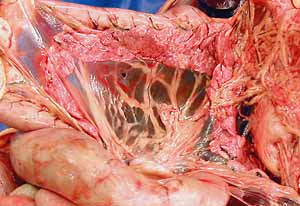 |
 |
2 |
| 3 |  |
 |
4 |
| 5 |  |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 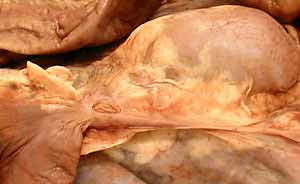 |
 |
8 |
| 9 |  |
 |
10 |