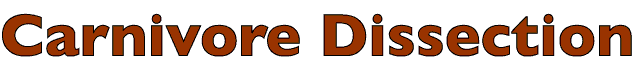
LAB 16 Introduction
Abdominal & Peritoneal Cavities
and Abdominal Viscera
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 155-165)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Open the abdominal cavity and identify peritoneal structures:
- falciform ligament and the median ligament of the urinary bladder
- vaginal ring (and its relationship to the inguinal canal & canal contents)
- greater omentum (including the omental bursa & gastrosplenic ligament)
• Regions and openings of the diaphragm:
- tendinous center
- diaphragm muscle regions (right/left crus; costal & sternal)
- openings (aortic hiatus; esophageal hiatus; caval foramen)
• Identify lobes of the liver, the gallbladder and associated ducts
• Examine alimentary tract viscera:
- stomach (including its curvatures, regions, and sphincters)
- duodenum (descending, ascending, and flexures)
- jejunum and mesenteric lymph nodes
- ileum and the ileal (ileocolic) orifice
- cecum and the cecocolic orfice
- colon (ascending, transverse, and descending)
- rectum
• Also, find:
- urinary bladder
- duodenum (descending, ascending, and flexures)
- spleen
female:
- uterus (cervix, body, & bilateral uterine horns)
male:
- ductus deferens (bilateral)
Anatomical Terms:
Abdominal & Peritoneal Cavities
transversalis fascia
parietal & visceral peritoneum
falciform ligament (fat filled)
round ligament of the liver
median ligament of the bladder
vaginal ring
deep inguinal ring
ductus deferens
caudal epigastric a. & v.
Abdominal Viscera
greater omentum
omental bursa
urinary bladder [palpate]
uterus [palpate] (cervix, body, uterine horns)
spleen [palpate]
gastrosplenic ligament
diaphragm
tendinous center
lumbar part (left crus & right crus)
costal part
sternal part
cupula
aortic hiatus
esophageal hiatus
caval foramen
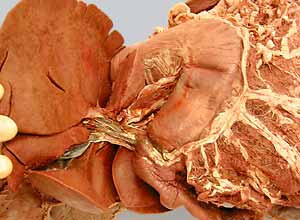
liver
right medial & lateral lobes
quadrate lobe
left medial & lateral lobes
caudate lobe
caudate process (with renal impression)
papillary process
hepatic ducts
gallbladder
cystic duct
bile duct
stomach
cardiac part
fundus
body
pyloric part
pyloric antrum
pyloric canal
pylorus (spincter)
greater & lesser curvatures
Small Intestines:
duodenum
cranial duodenal flexure
descending part
caudal duodenal flexure
ascending part
duodenojejunal flexure
jejunum
mesenteric lymph nodes (in mesojejunum & mesoileum)
ileum
ileal orifice (ileocolic orifice)
Large Intestines:
cecum
cecocolic orifice (dog, indistinct in cat)
colon (ascending, transverse & descending [palpate] )
right & left colic flexures
rectum
Note:
ileum [Latin] = distal end of the small intestines
ilium [Latin] = the most cranial bone of the os coxae
pylorus [Greek: pyloros] from pyle = gate and ouros = guard
Instructor Commentary:
The mesojejunum and mesoileum (collectively known as the "mesentery") rotate 360 degrees around the axis of the cranial mesenteric artery during embryonic development. This rotation creates a narrow "root of the mesentery" (surrounding the cranial mesenteric artery).
The gross anatomical distinction between jejunum and ileum is remarkably different for human vs. veterinary anatomists. Human anatomists regard "jejunum" as the cranial 40% and "ileum" and the caudal 60% of the combined jejunum-ileum. Veterinary anatomists regard "ileum" as the short terminal segment of the small intestines, demarcated by the ileocecal fold and the presence of vessels on the intestinal anti-mesenteric surface. Although the jejunum and ileum exhibit differences histologically, there is not a distinct gross anatomical difference between them, beyond the anti-mesenteric vessels.
Lumbar musculature of the diaphragm, which attaches to bodies of lumbar vertebrae, is designated left crus and right crus, implying that the attachments are "legs" of the diaphragm. Two structures pass between the two crura: the aorta (through the aortic hiatus) and the esophagus (through the esophageal hiatus).
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
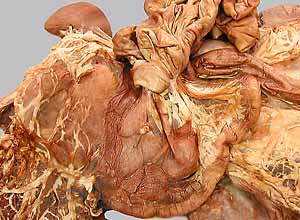
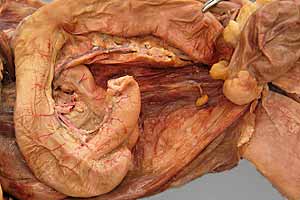
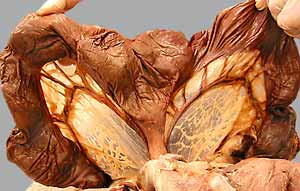
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 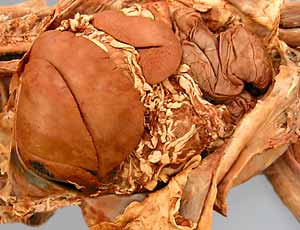 |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 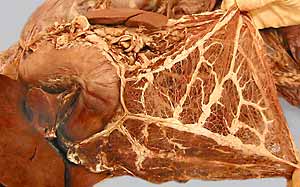 |
 |
4 |
| 5 |  |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 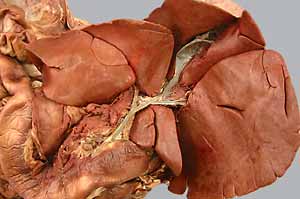 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 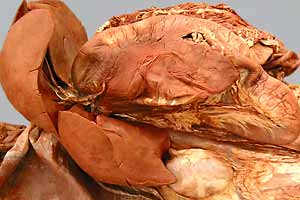 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 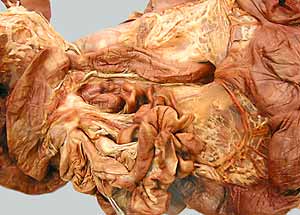 |
 |
12 |
| 13 | 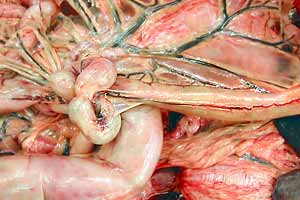 |
 |
14 |