Region: Head & Neck
CONTENTS:
List of Anomalies:
• Cleft Palate
• Cleft Lip (Hare Lip)
• Cyclopia & Microphthalmia
• Brachycephalic Syndrome
• Occipito-atlantal Malformation
Anomalies Commentary:
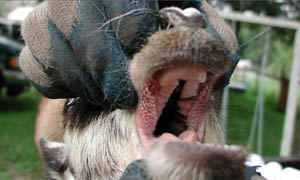
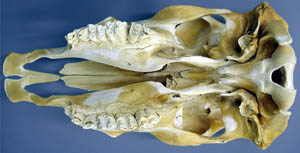
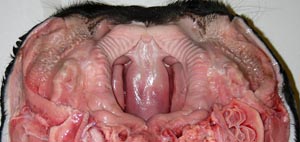
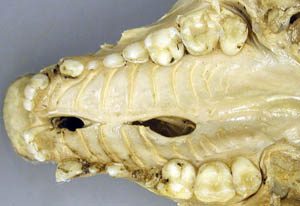
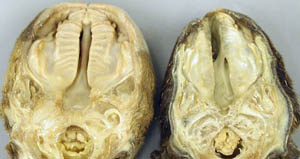
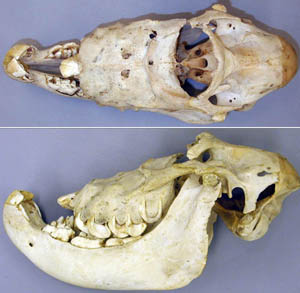
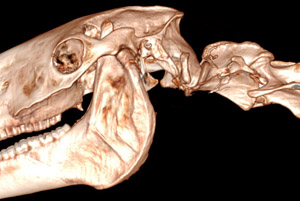
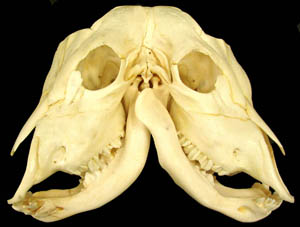
Palatoschisis is the technical term for cleft palate [schist- = split as in schistosomus reflexus]. Cleft palates can be unilateral or bilateral. The bilateral type is symmetrical and the ventral edge of the nasal septum is easily seen. In the unilateral type the ventral edge of the nasal septum is fused to the normal side hard palate so that it is hard to see.
Bilateral cleft palate is more common than unilateral and unilateral is usually associated with incomplete clefts and cleft lip (hare lip because it resembles the upper lip of a hare). In animals cleft palate is far more common than cleft lip. The University of Minnesota museum collection has 18 cleft palate specimens but only 2 of them have a cleft lip. Cleft palate may occur associated with other defects such as dicephalus or achondroplasia or it may not be associated with other defects. In our collection 7 of 18 cleft palates were associated with other defects.
The Kentucky study of equine congenital defects found 24 cases of cleft palate in 608 foals with defects (AJVR 46:353-358, 1985). In contrast, a multispecies study of congenital defects found only 40 cleft palates among 6,455 animals with congenital defects (AJVR 31:1871-1879, 1970).
The human incidence of cleft lip is one in 1000 live births and for cleft palate the incidence is one in 2500 live births. The risk of cleft palate increases to 2% for a sibling of a child with the condition. When a parent and a child have cleft palate the risk for the next sibling is 15%. A significant association has been found between maternal cigarette use during pregnancy and having a child with cleft lip/palate (Plas. & Recons. Surg. 105(2):485-91, 2000). The risk of cleft palate appears to be more common in underdeveloped countries than in so called developed countries and the difference might be associated with ingestion of plant toxins.
Several plant alkaloids induce cleft palate when ruminant dams are exposed to the teratogens during gestation. These plants include lupines, poison hemlock and Nicotiana spp. (J Nat Toxins 8(1):117-134, 1999). The critical period is 35 to 40 days gestation in sheep and goats and 40-50 days in cattle. Goats are more susceptible than sheep to the toxins and an even higher incidence of joint deformities occur in exposed animals. Ultrasound studies have shown depressed fetal movements due to the plant toxins (KE Panter, personal communication). Failure of extension of the head leads to cleft palate because the tongue is not pulled out of the space between the developing palatal shelves. This occurs when the head extends and the sternohyoideus m. pulls down on the basihyoid bone to which the tongue is attached.
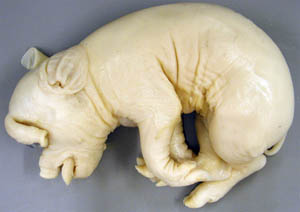
Cyclopia means "round eye or cycle eye". In the Greek mythology of Homer the Cyclopes were one eyed cannibal giants on a remote isle. Cyclops specimens have a single midline orbit and a single or fused eye. The nasal cavity is not developed and the face is foreshortened so that the mandible protrudes. In some cases there is a trunk like proboscis which is attached to the head dorsal to the single eye. The best studied cyclops malformation is that of lambs whose dams were exposed to the plant toxins from Veratrum californicum during the 14th day of gestation. (Noden DM and DeLahunta A, The Embryology of Domestic Animals, Williams and Wilkins, 1985). This is quite early in comparison with the 35-40 day critical period of gestation for cleft palate in sheep.
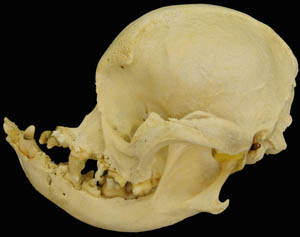
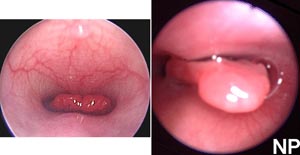
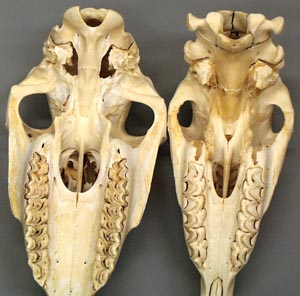
Brachycephalic syndrome in dogs is characterized by a short maxilla in contrast to a longer mandible. Most often affected breeds are English bulldogs, pugs and Boston terriers. Associated defects may include an elongated soft palate, stenotic nares, everted laryngeal ventricles and hypoplastic trachea (JAVMA 230:1324-1328, 2007). Clinical signs involve respiratory distress. The short nasal cavity shifts the nasal conchas (turbinates) caudally so that the choanal passages are blocked by the conchas. These caudally shifted conchas can be observed in the nasopharynx by endoscopy. Surgical correction may include the nares, soft palate and laryngeal ventricles.
Anomaly Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 |  |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 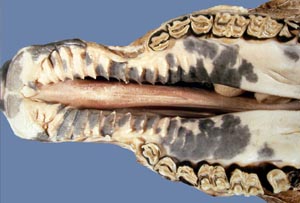 |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 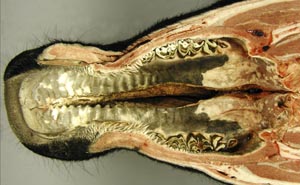 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 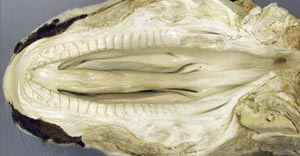 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 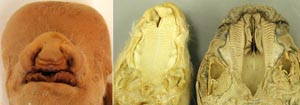 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 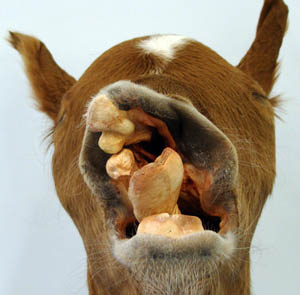 |
 |
12 |
| 13 | 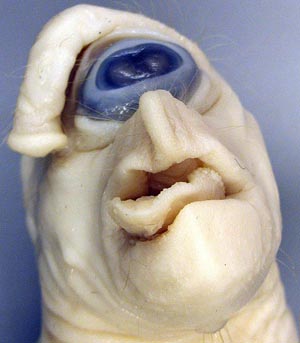 |
 |
14 |
| 15 | 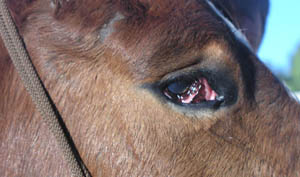 |
 |
16 |
| 17 | 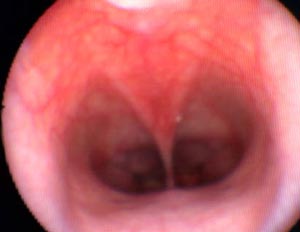 |
 |
18 |
| 19 | 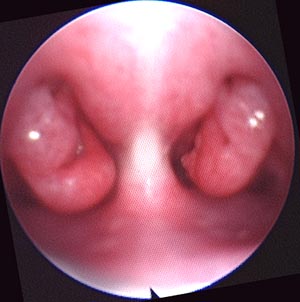 |
 |
20 |
| 21 | 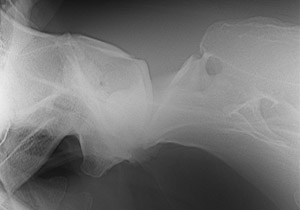 |
 |
22 |
| 23 |  |
 |
24 |
| 25 |  |
 |
26 |
