LAB 17 Genitalia
Study of Genitalia Specimens, isolated and in situ
Lab Objectives:
• Study the parts of the testicle and be able to differentiate right versus left testicles.
• Trace the ductus deferens to the genital fold and the ampullae. Then identify the other accessory sex glands in all available species.
• Identify the urethralis, ischiocavernosus and bulbospongious muscles and note that urethralis muscle fibers partially cover the bulbourethral glands.
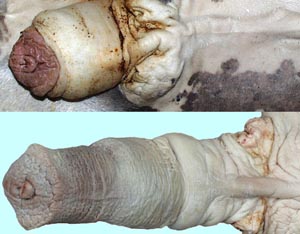
• On equine specimens note the layers of the prepuce and the preputial ring. Then identify the glans penis, urethral process, fossa glandis and the small opening of the urethral sinus. Observe the urethral sinus on a midline sectioned demonstration specimen.
• On ruminant and porcine specimens note the retractor penis muscle and its attachments. Identify the parts of the penile sigmoid flexure and the elongated urethral process of small ruminant males.
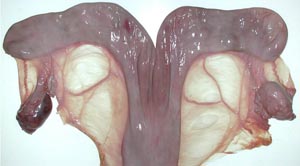
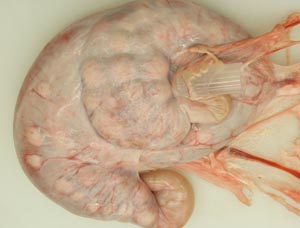
• On the mare ovary note the ovulation fossa and smooth surface. On bovine ovaries note the elevated corpra lutea and follicles. Observe the ovarian bursa of all available species and identify the uterine tube, mesovarium, mesosalpinx and antimesosalpinx.
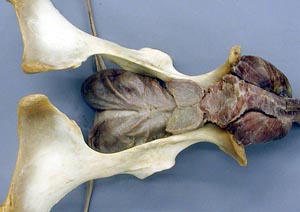
• Identify the broad ligament, the uterine horns and the bovine intercornual ligament. On mare tracts find the round ligament of the uterus which has a characteristic "tag".
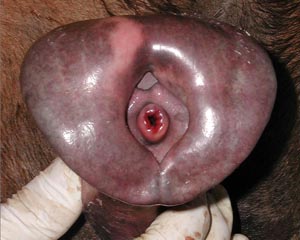
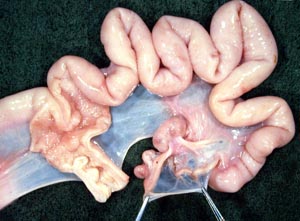
• Make a dorsal incision from the vulva to the uterine body to expose the lumen of the female genital tract. Note the urethral orifice in all species and find the suburethral diverticulum in cow and sow tracts. Compare and contrast the cervical canal of all available specimens.
Anatomical Terms:
Male Genitalia & Associated Structures
cremaster m.
parietal vaginal tunic
mesorchium
mesoductus
visceral vaginal tunic
testicle
epididymis
head
body
tail
testicular bursa
(be able to differentiate right & left testicles)
genital fold
uterus masculinus
ductus deferens
ampulla
vesicular glands
body of the prostate
urethralis m.
preputial ring
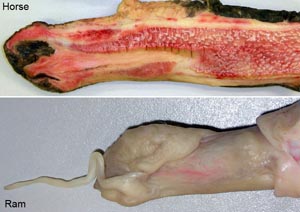
glans penis
urethral process
fossa glandis
urethral sinus
ischiocavernosus m.
corpus cavernosum penis
bulbospongiosus m.
corpus spongiosum penis
retractor penis m.
tunica albuginea
crus of the penis ("pizzle eye" in bovine)
sigmoid flexure (bov, por)
proximal loop
distal loop
dorsal a. of the penis
dorsal n. of the penis
prepuce
preputial muscle
cranial preputial m.
bulbourethral glands
preputial diverticulum (por)
Female Genitalia & Associated Structures
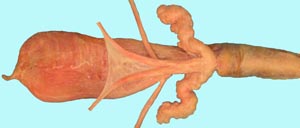
ovary
ovulation fossa
ovarian bursa
corpus lutem
ovarian proper ligament
mesosalpinx
uterine tube
infundibulum
uterus
uterine horns
uterine body
intercornual ligament (bov)
placentomes
cervix
external os of the cervix
transverse folds of the cervix (bov)
mucosal prominences (por)
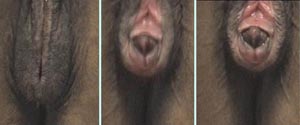
vulva
dorsal & ventral commissures
clitoris
clitoral fossa
vestibule
vagina
urethra
urethral orifice
suburethral diverticulum (bov)
ovarian a.
ovarian v.
(uterine a.)
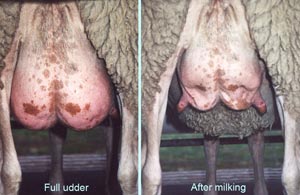
Mammary Gland Structures
medial suspensory ligament
lateral laminae
external pudendal vessels
venous ring
subcutaneous abdominal ("milk") veins = cranial & caudal superficial epigastric vv.
supernumerary teats
teat orifice
papillary duct
lactiferous sinus
teat sinus
gland sinus
lactiferous ducts
mammary lymph node/superficial inguinal lymph node
Instructor Commentary:
Several structures have different names for anatomists and clinicians or animal scientists. The ductus deferens of anatomy is often called vas deferens in the clinic but anatomists restrict use of the term vas to vessels. The clinical term oviduct is replaced by uterine tube in the anatomical literature and in human medicine the term tubal ligation is often used.
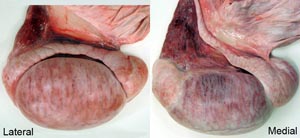
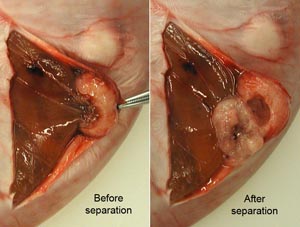
In common usage the term testicle refers to the testis plus the epididymis and the first part of the ductus deferens. In short, the testicle is what is removed by castration. Since cryptorchid castration is common in horses, differentiation of right and left testicles is important when only one descended testicle is found so that the surgeon knows where to look for the undescended testicle. By identifying the epididymis on the lateral side, ductus deferens on the medial side and the tail of the epididymis caudally, a testicle can be oriented so that left v. right can be determined.
The retractor penis muscle is of little functional significance in the male horse but in the bull and boar it attaches distal to distal loop of the penile sigmoid flexure and it is responsible for pulling the extended penis into the S shaped curve, the sigmoid flexure. A slaughterhouse steer penis can be used to demonstrate the action of the retractor muscle by holding the upper part of the penis firm on a table while pulling the retractor muscle with the other hand. Clinically, a pudendal nerve block will relax the retractor penis muscle and allow the penis to drop out of the prepuce for examination and treatment.
The mesosalpinx is the mesentery of the uterine tube. It has a free border known as the antimesosalpinx. The ovarian bursa is a space between the mesentery of the ovary (mesovarium) and the mesosalpinx. The opening of the ovarian bursa is tiny in carnivores but an examiner can pass several fingers into the bursa of mare, cow or sow.
The urethral orifice marks the junction of the vestibule with the vagina. Ruminants and the sow have a suburethral diverticulum ventral and caudal to the urethral orifice. When passing a urethral cannula this diverticulum should be filled with a finger to prevent the cannula from entering the diverticulum and to guide it into the urethral orifice.
The bovine cervix has several transverse rings that make passage of an AI (artificial insemination) pipet difficult but no such structures are found in the mare. The sow cervix is elongated and has numerous mushroom shaped mucosa prominences. Note: the penis of the ram and billy goat has a long thin urethral process that was thought to assist the entry of semen into the cervical canal during mating but experimental removal of the urethral process does not affect the rate of conception..
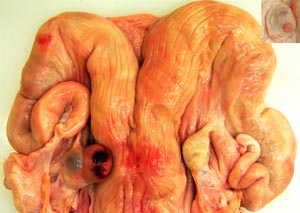
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 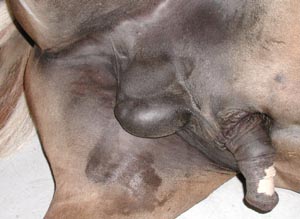 |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 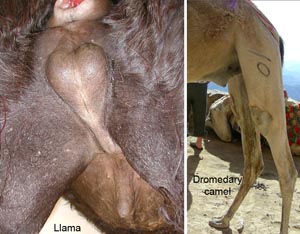 |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 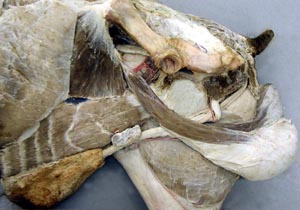 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 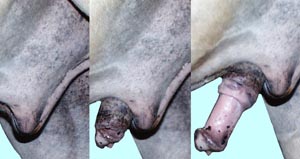 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 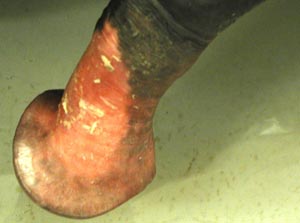 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 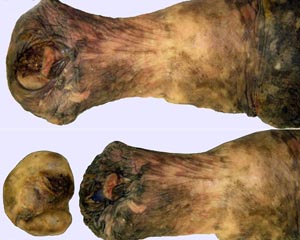 |
 |
12 |
| 13 |  |
 |
14 |
| 15 | 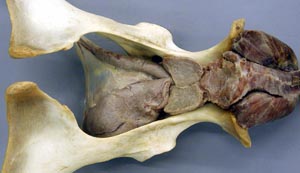 |
 |
16 |
| 17 | 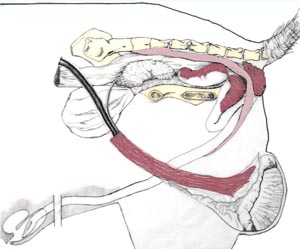 |
 |
18 |
| 19 | 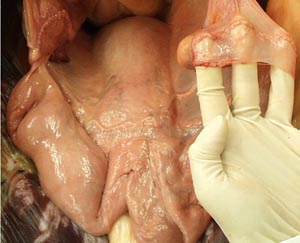 |
 |
20 |
| 21 | 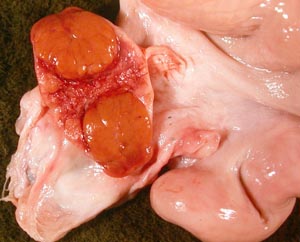 |
 |
22 |
| 23 | 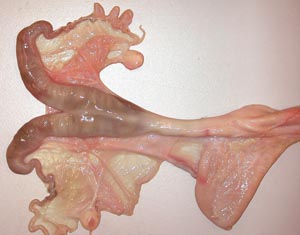 |
 |
24 |
| 25 | 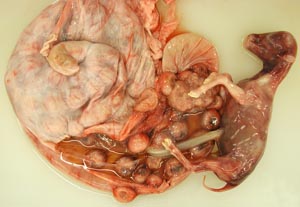 |
 |
26 |
| 27 | 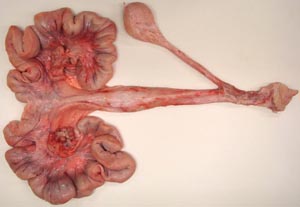 |
 |
28 |
| 29 | 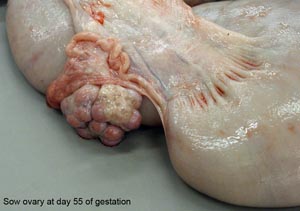 |
 |
30 |
| 31 |  |
 |
32 |
