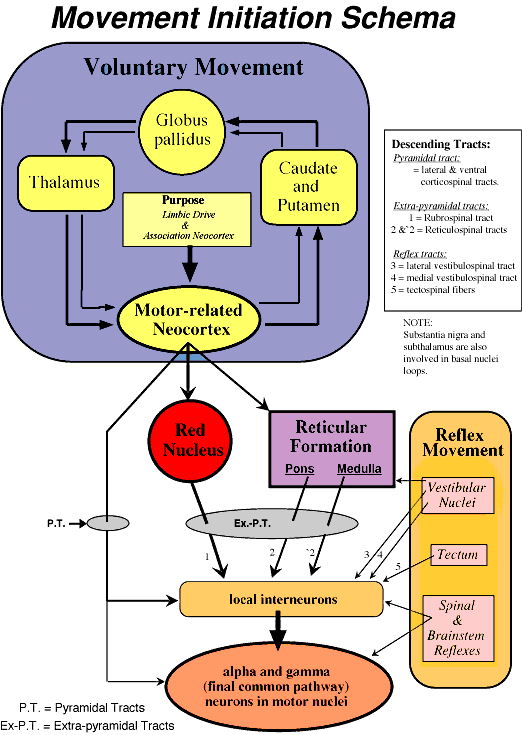
Movement Schematic
The following diagram shows that:
• voluntary movement is initiated by circuits located in the forebrain
• the cerebral cortex can use the pyramidal tract and/or extra-pyramidal tracts for voluntary movement
• voluntary tracts and reflex tracts simultaneouly compete for control of local interneurons
• final common pathway neurons are controlled mainly via interneurons.