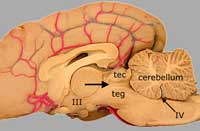
The mesencephalon, which gives rise to oculomotor (III) and trochlear (IV) cranial nerves, contains the mesencephalic aqueduct. The periaqueductal gray matter that surrounds the aqueduct plays an important role in pain modulation.
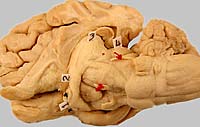
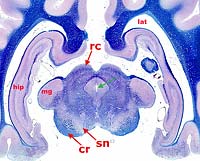
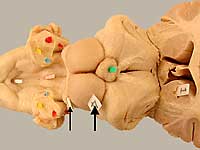
The midbrain region dorsal to the mesencephalic aqueduct is termed the tectum (roof) of the midbrain. It consists of bilateral rostral and caudal colliculi (elevations). The rostral colliculus is a visual reflex center. The caudal colliculus is an auditory reflex center.
Fibers located along the ventral surface of the midbrain constitute the crus cerebri . Nerve fibers within the crus cerebri come, via the internal capsule, from neuron cell bodies located in the cerebral cortex. Axons in the crus cerebri convey voluntary motor commands to the spinal cord.
Immediately dorsal to the crus cerebri, identify the gray matter called substantia nigra. (In humans the substantia nigra has pigmented neurons and the loss of these neurons results in Parkinson's disease.) The region between the substantia nigra and the tectum is called the tegmentum. It contains a mixture of gray and white matter.