
Neurons - Image 8
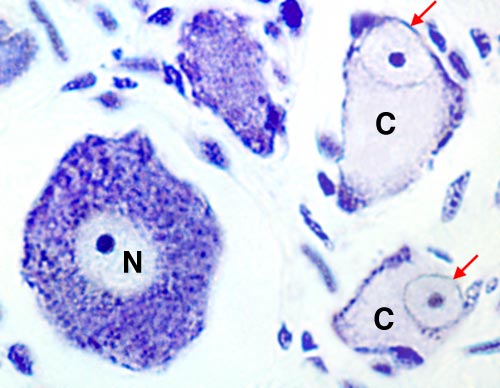
Two chromatolytic cell bodies (C) are adjacent to a normal cell body (N, placed over the nucleus). Chromatolysis is a cell body reaction to neuronal injury, such as axonal transection some distance from the cell body. Features of neuron chromatolysis include a swollen cell body, eccentric displacement of the nucleus, and loss of Nissl substance except along the margins of the cell body. Pathologists search for chromatolysis as evidence of nervous system injury. Particularly in the past, researchers used axon transection and the resultant cell body chromatolysis to trace neural pathways.