|
|
|
 |
|
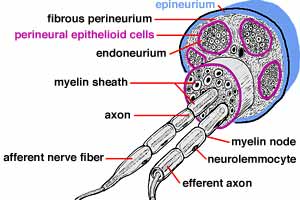
PNS - Image 1:
Artist illustration of the connective tissue associated with a peripheral nerve. Nerves are composed of nerve fascicles. The entire nerve is enveloped by connective tissue called epineurium. Individual fascicles are delineated by perineurium. Layers of flattened mesodermal cells, called perineural epithelium (epithelioid) cells, line the perineurium. Connective tissue inside perineural epithelium is called endoneurium. |
|
|
|
 |
|
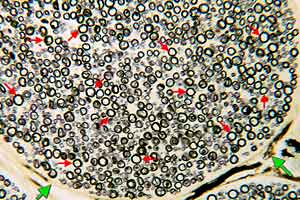
PNS - Image 2:
ransverse section through a nerve fascicle (Wolter myelin stain). Myelin sheaths (red arrows) are stained black. Because of lipid composition, perineural epithelium (green arrows) stains slightly. |
|
|
|
 |
|
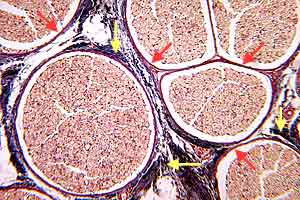
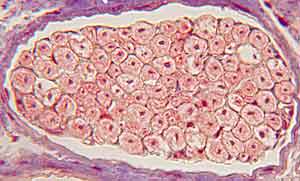
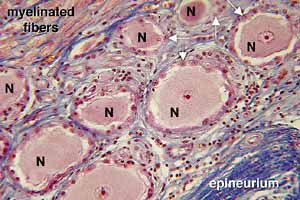
PNS - Image 3:
Transverse section through a peripheral nerve (Triple stain). Several nerve fascicles are visible. Each fascicle is surrounded by perineural epithelium (red arrows). Fibrous perineurium (yellow arrows) is outside of the perineural epithelium.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
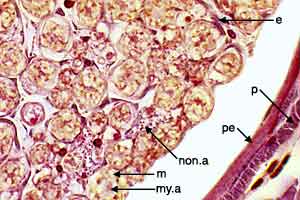
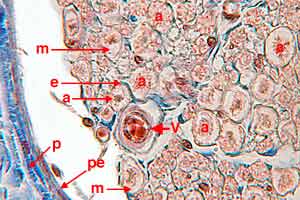
PNS - Image 4:
High power view of the margin of a nerve fascicle (silver stain). Non-myelinated axons (non.a) appear as clusters of dots. Myelinated axons (my.a) are each surrounded by myelin sheath (m). The fascicle is delineated by perineural epithelium (pe) inside fibrous perineurium (p).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 5:
High power view of the margin of a nerve fascicle (Triple stain). Myelinated axons (a) are each surrounded by myelin sheath (m). Blue endoneurium (e) is evident within the fascicle. The nerve fascicle is delineated by perineural epithelium (pe) inside fibrous perineurium (p).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
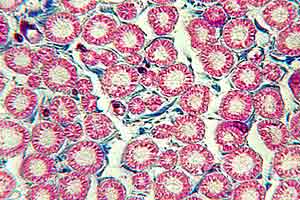
PNS - Image 6:
Transverse section through myelinated fibers within a nerve fascicle (Triple stain). Blue endoneurium surrounds myelin sheaths. Myelin neurokeratin appears as well defined red circles.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
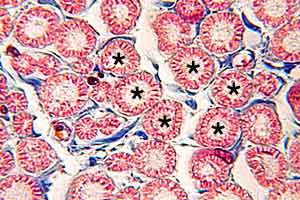
PNS - Image 7:
Transverse section through myelinated fibers within a nerve fascicle (Triple stain), a higher power view of the preceding section. Blue endoneurium surrounds myelin sheaths. Myelin neurokeratin appears as well defined red circles. Axons (asterisks) within myelin rings generally are not distinct with this stain. |
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 8:
Transverse section through myelinated fibers of a ventral root (silver stain). Axons are distinct within myelin sheaths (neurokertatin). Ventral roots are are covered by meninges (pia mater).
|
|
|
|
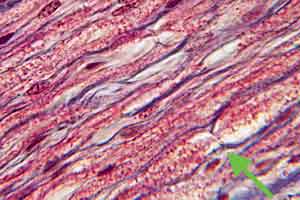 |
|
PNS - Image 9:
Longitudinal section through myelinated fibers within a nerve fascicle (Triple stain). An axon (asterisk) and a myelin node (arrow) are labeled. Myelin neurokeratin is red. Endoneurium is blue.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
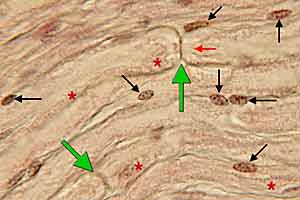
PNS - Image 10:
High power view of a longitudinal section through a nerve fascicle. An axon (red arrow) and two myelin nodes (green arrows) are labeled. Myelin neurokeratin is indicated by red asterisks. Lemmocyte cell nuclei are labeled with black arrows.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 11:
Longitudinal section through part of a spinal ganglion (Triple stain). Unipolar cell bodies (N) can be seen superficial to dorsal root nerve fibers (myelinated fibers) and deep to epineurium of a spinal nerve. Each cell body has a central nucleus and is surrounded by a well-defined capsule of satellite glial cells (arrows).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
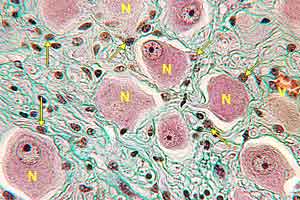
PNS - Image 12:
Section through part of an autonomic ganglion (Triple stain). Multipolar neuron cell bodies (N) are within poorly-defined capsules formed by satellite glial cells (arrows).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 13:
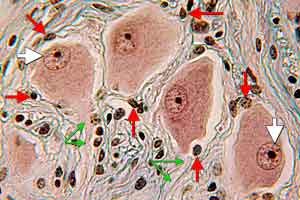
High power view of a section through part of an autonomic ganglion (Triple stain). Multipolar neuron cell bodies with eccentric nuclei (white arrows) are within poorly-defined capsules formed by satellite glial cells (red arrows). Axons (green arrows) can be seen leaving cell bodies.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 14:
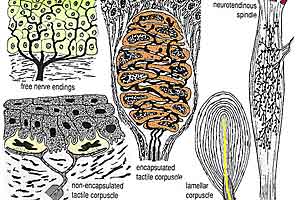
Schematic illustration of receptors. Free nerve endings (upper left) are shown extending into the epidermis. Tactile corpuscles (lower left) involve epidermal cells transformed into sensory cells by nerve endings. Encapsulated receptors (right) consist of nerve endings encapsulated by lemmocytes and perineural epithelium.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 15:
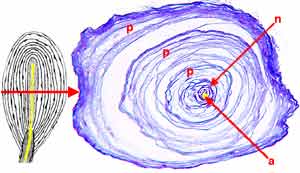
Pacinian (lamellar ) corpuscle. Left: Schematic illustration of a lamellar corpuscle sectioned longitudinally. The axon (yellow) is surrounded immediately by lemmocytes, in turn surrounded by perineural epithelium. The red arrow points to a transection at the level indicated. Right: Transverse section through an actual Pacinian corpuscle.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
PNS - Image 16:
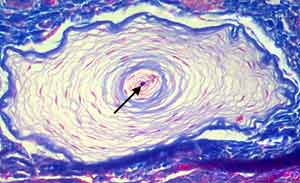
Transverse section through a Pacinian (lamellar ) corpuscle from a feline urethra (Triple stain). The axon (arrow) is surrounded immediately by lemmocytes which, in turn, are surrounded by perineural epithelium.
|
