Close
Canine Prostatic Urethra
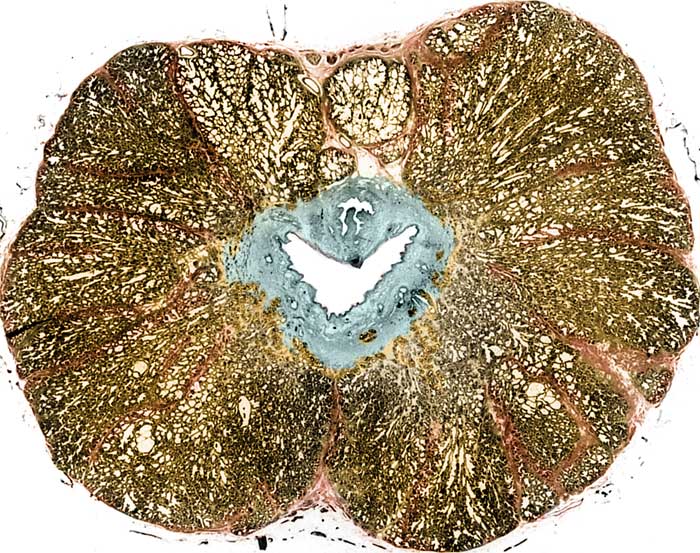
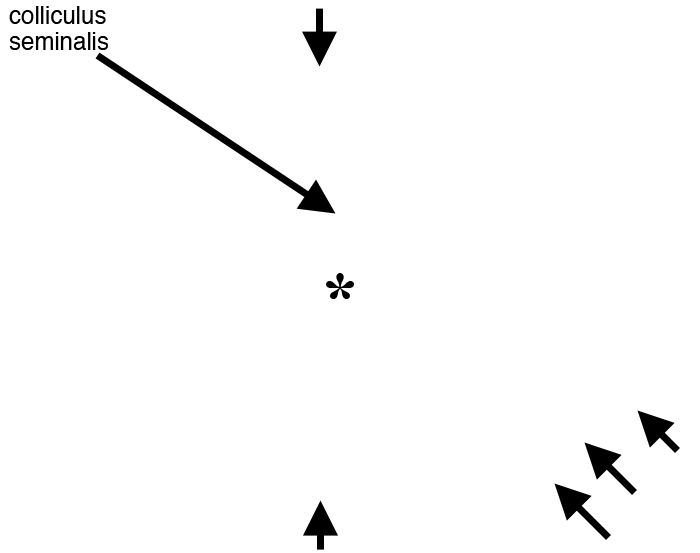
Above: Transverse section through the prostatic urethra of a dog (color added). The prostate gland is bi-lobed and completely encircles the urethra. Each lobe is composed of lobules partitioned by trabeculae. The urethral lumen (asterisk) is surrounded by a combined lamina propria-submucosa (blue).
The colliculus seminalis produces a bulge in the dorsal submucosa. Smooth muscle has an insignificant sphincter role at this level, none surrounds the urethral lumen. Small amounts of smooth muscle are present on the surface of the prostate and within trabeculae partitioning prostatic lobules (arrows).
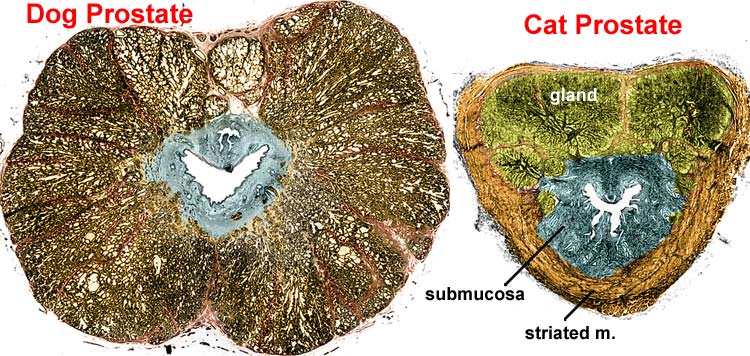
Below: Canine and feline prostate glands are compared in transverse sections through prostatic urethrae. Both prostate glands are bi-lobed but the feline gland is relatively small and positioned dorsal to the urethra.
Below: Canine and feline prostate glands are compared in transverse sections through prostatic urethrae. Both prostate glands are bi-lobed but the feline gland is relatively small and positioned dorsal to the urethra.
[spacebar toggles labels — esc closes window]
