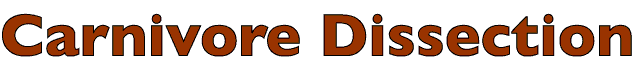
LAB 20 Introduction
Pelvic Limb Vessels
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 197-205)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Remove skin from the pelvis and thigh. Reflect superficial and middle gluteal muscles on the right side.
Later, reflect skin from the crus and hock to observe subcutaneous and deep vessels.
• Trace the distribution of the caudal gluteal artery to the pelvic wall:
- the cranial gluteal artery & the iliolumbar artery supply gluteal muscles
• Identify the external iliac artery and its deep femoral branch:
- pudendoepigastric trunk from deep femoral a.
-- caudal epigastrtic artery & external pudendal artery
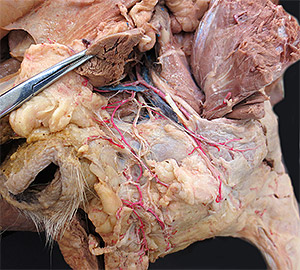
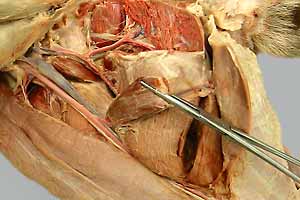
• Examine the femoral artery and its major branches:
- proximal, middle, & distal caudal femoral arteries
- saphenous artery and descending genicular artery
(Transect & reflect muscles to see the following arteries)
- popliteal artery = femoral artery re-named in stifle region
-- cranial tibial artery = main source of blood to the pes
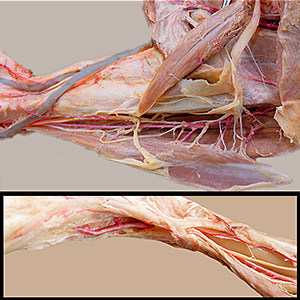
• Examine medial and lateral saphenous veins.
Anatomical Terms:
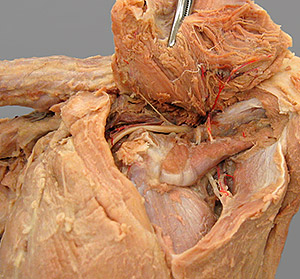
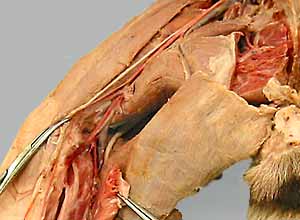
Pelvic limb: arteries
caudal gluteal a. (branch of internal iliac a.)
cranial gluteal a. [& nerve]
iliolumbar a.
external iliac a. (to level of vascular lacuna)
deep femoral artery
pudendoepigastric trunk
caudal epigastric a.
external pudendal a.
medial circumflex femoral a.
deep & transverse branches
femoral triangle [palpate]
femoral a. (begins at level of vascular lacuna) [palpate & take pulse]
superficial circumflex iliac a.
lateral circumflex femoral a.
proximal caudal femoral a.
saphenous a. [palpate]
cranial & caudal branches [palpate & take pulse]
descending genicular a.
middle caudal femoral a.
distal caudal femoral a.
popliteal a.
cranial tibial a.
Pelvic limb: superficial veins
medial saphenous v. (feline venipuncture site) [palpate]
lateral saphenous v.
cranial branch (canine venipuncture site) [palpate]
Note:
The following two terms pertain to the knee:
popliteal, from Latin: poples = ham
genicular, from Latin: geniculatus = bent like a knee
Instructor Commentary:
Superficial veins are accessible sites for obtaining blood samples or administering intravenous drugs. The medial saphenous vein is a preferred site for venipuncture in the cat. In the dog, the cranial branch of the lateral saphenous vein is the most prominent of the superficial veins. However, because the vein is relatively mobile it is not easy to penetrate. Thus the cephalic vein is the first choice for intravenous injection even though it is a less visible site. The external jugular vein is the first choice for drawing large amounts of blood.
The femoral triangle, where the femoral artery and vein are subcutaneous, represents a site where the pulse is easily taken, where arterial blood can be sampled, and where the arterial tree can be cannulated for experimental or special diagnostic procedures.
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
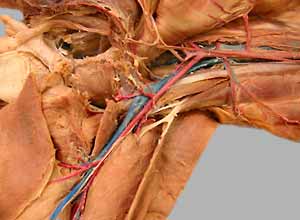
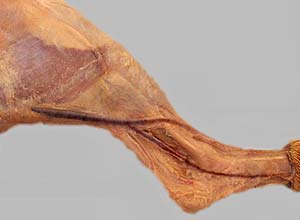
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 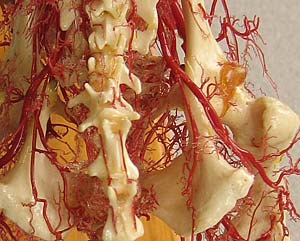 |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 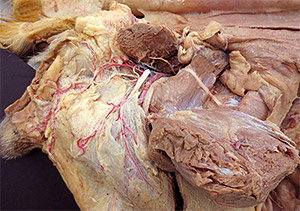 |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 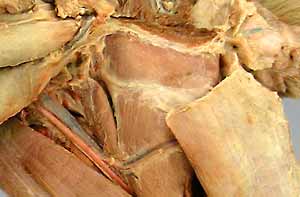 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 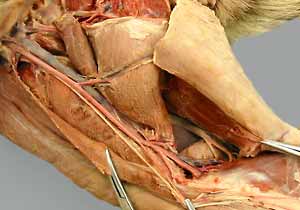 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 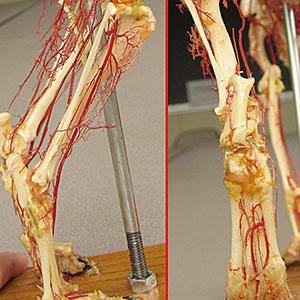 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 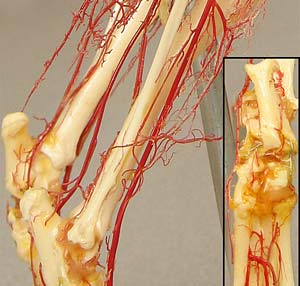 |
 |
12 |
| 13 | 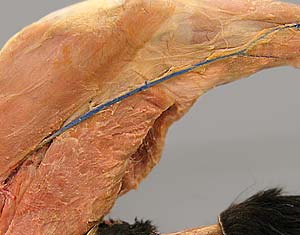 |
 |
14 |