Reticular Formation Nuclei
CLOSE
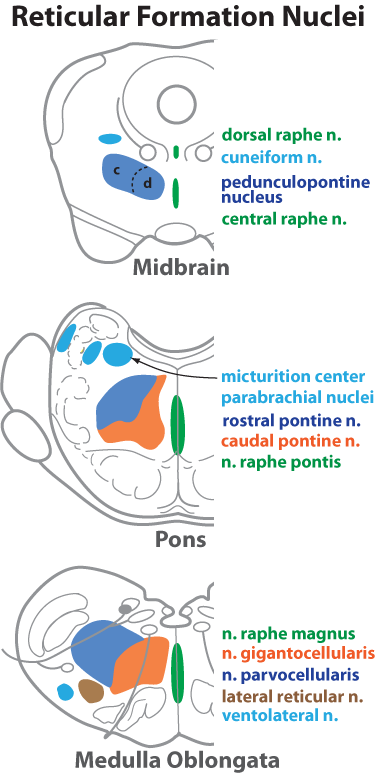
Figure 18—6. Schematic drawing showing selected nuclei of the reticular formation. Reticular formation nuclei are organized into longitudinal columns. Unpaired, midline, raphe nuclei (green) contain neurons that release serotonin. Medial column nuclei (orange) have large (magnocellular) neurons and gives rise to reticulospinal axons. Nuclei comprising the lateral column (dark blue) generally have small (parvocellular) neurons. The small neurons are activated by collateral branches from sensory tracts; their axons synapase on the large neurons in the medial column. Some lateral reticular nuclei have visceral roles (pale blue). Some reticular nuclei project to the cerebellum (brown). The pedunculopontine nucleus of the midbrain has compact (c) and diffuse (d) regions. The former has large cholinergic neurons that project axons to the thalamus. The latter connects to basal nuclei circuits.
Go Top