Red Nucleus
CLOSE
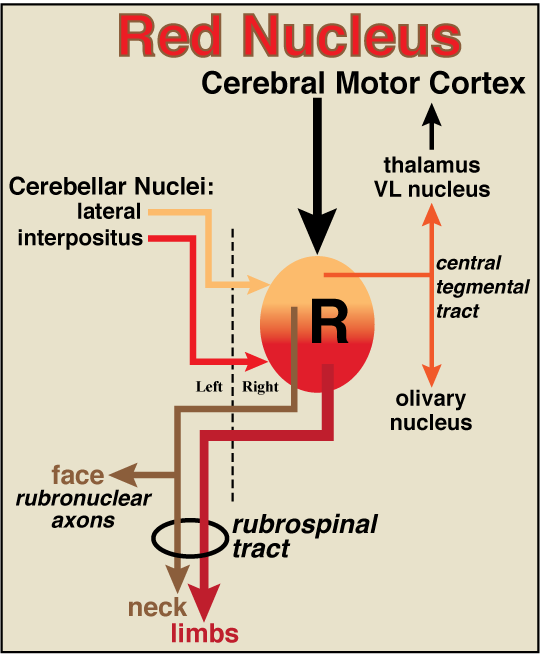
Figure 18—20. Schematic illustration of a right-side red nucleus (R), including major projections and input connections. The canine red nucleus exhibits a gradient of cell sizes, ranging from large neurons (magnocellular region) concentrated caudally (red region) to small neurons (parvicellular region) concentrated rostrally (yellow region). Rubrospinal tract axons that arise from the large projection neurons (red) decussate and terminate on interneurons associated with limb motor units. Rubrospinal axons from medium projection neurons (brown) decussate and terminate in the cervical spinal cord or in cranial nerve nuclei (rubronuclear axons). Small neurons located rostrally in the red nucleus send axons ipsilaterally to the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus and the olivary nucleus via the central tegmental tract (orange). All projection neurons are driven by the ipsilateral motor cortex. The cerebellar interpositus nucleus excites large neurons. The lateral (dentate) cerebellar nucleus excites small and medium size neurons. The dashed line indicates the midline.
Go Top