Otic Ganglion Drawing
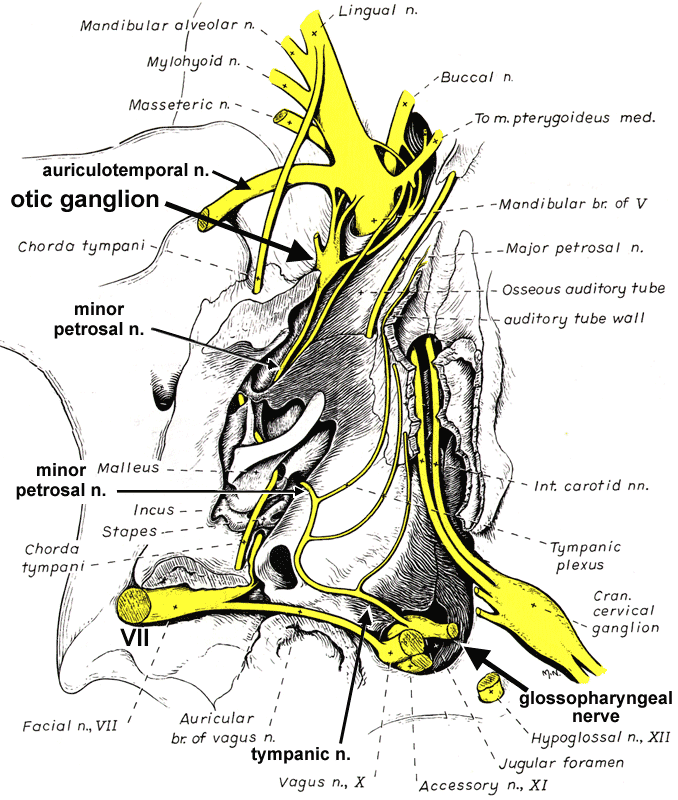
Ventral view drawing of the cavity of the middle ear following removal of the tympanic bulla, from Miller's Anatomy of the Dog textbook. The otic ganglion is named for its location close to the ear.
The otic ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionic input from the glossopharyngeal nerve via nerves that run through the middle ear: The tympanic nerve gives off tympanic plexus branches and is continued as the minor petrosal nerve which connects to the otic ganglion. The ganglion sends postganglionic branches to the parotid salivary gland, via the auriculotemporsal nerve, and the zygomatic salivary gland, via a buccal branch of the mandibular nerve.
The otic ganglion receives parasympathetic preganglionic input from the glossopharyngeal nerve via nerves that run through the middle ear: The tympanic nerve gives off tympanic plexus branches and is continued as the minor petrosal nerve which connects to the otic ganglion. The ganglion sends postganglionic branches to the parotid salivary gland, via the auriculotemporsal nerve, and the zygomatic salivary gland, via a buccal branch of the mandibular nerve.
[spacebar toggles labels — esc closes window]