Parasympathetic Branches of the Facial Nerve
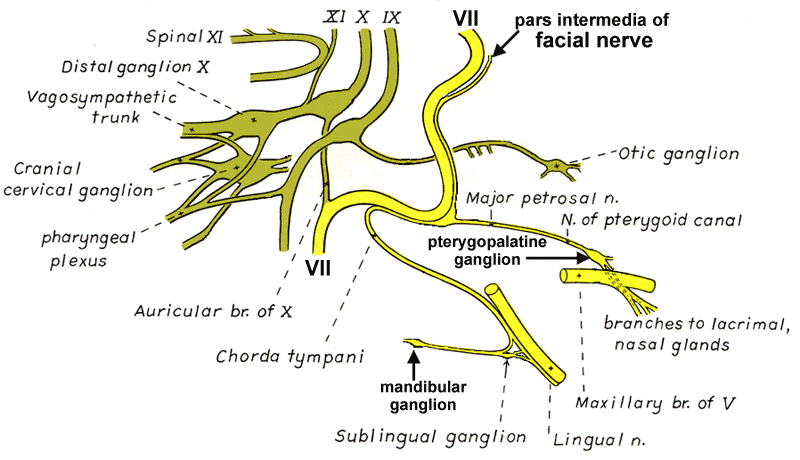
Drawing of selected cranial nerve branches from Miller's Anatomy of the Dog textbook. The facial nerve pars intermedia is the sensory and parasympathetic component of the facial nerve, which otherwse contains somatic efferent nerve fibers.
For nasal and lacrimal gland innervation, preganglionic parasymapthetic axons run in the major petrosal nerve (which leaves the facial nerve at the site of the geniculate ganglion within the petrous temporal bone. The preganglionic axons synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. The ganglion sends postganglionic branches to the orbit to innervate the lacrimal gland and branches to the maxillary nerve to innervate nasal glands.
To innervate mandibular and sublingual salivary glands, preganglionic parasymapthetic axons exit in the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve. The chorda tympani nerve (which also conveys taste afferents) arises within the petrous temporal bone and runs through the middle ear in order to join the lingual nerve. Preganglions axons leave the lingual nerve and synapse in the mandibular ganglion (and sublingual ganglion) located in the vicinity of the salivary glands.
For nasal and lacrimal gland innervation, preganglionic parasymapthetic axons run in the major petrosal nerve (which leaves the facial nerve at the site of the geniculate ganglion within the petrous temporal bone. The preganglionic axons synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. The ganglion sends postganglionic branches to the orbit to innervate the lacrimal gland and branches to the maxillary nerve to innervate nasal glands.
To innervate mandibular and sublingual salivary glands, preganglionic parasymapthetic axons exit in the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve. The chorda tympani nerve (which also conveys taste afferents) arises within the petrous temporal bone and runs through the middle ear in order to join the lingual nerve. Preganglions axons leave the lingual nerve and synapse in the mandibular ganglion (and sublingual ganglion) located in the vicinity of the salivary glands.
[spacebar toggles labels — esc closes window]