Canine Major Splanchnic Nerve
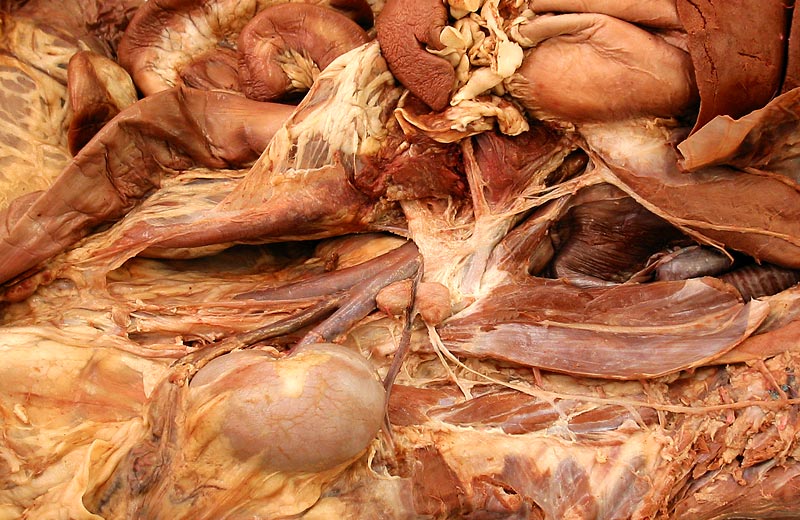
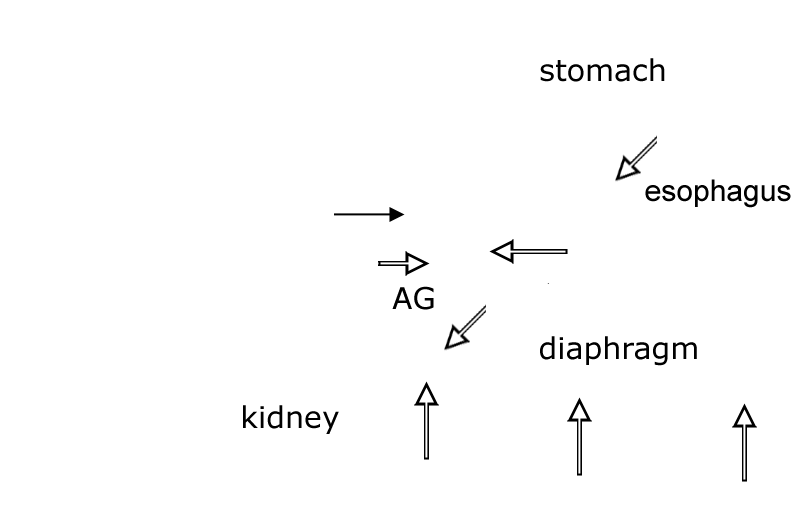
Left lateral view of a canine abdomen with much of the diaphragm removed. The major splanchnic nerve (maj splan n.) can be seen leaving the sympathetic trunk via two roots. (Two small minor spanchnic nerves are evident caudal to the major nerve.) The splanchnic nerves convey sympathetic preganglionic axons that innervate the medulla of the adrenal gland (AG) and ganglia within nerve plexuses covering the celiac and cranial mesenteric arteries. A left celiac ganglion is evident just cranial to the cranial mesenteric ganglion (g). The dorsal vagal nerve trunk (dor vag n trunk) can be seen joining the celiaco-mesenteric nerve plexus. Preganglionic parasympathetic axons from the vagal nerve trunk reach terminal ganglia in viscera by traveling in plexuses on arteries to the viscera. C eliac and cranial mesenteric arteries are labeled, as are the kidney, esophagus, stomach and spleen.
[spacebar toggles labels — esc closes window]