| Home Page |
General ANS Features |
Sympathetic Division |
Parasympathetic Division |
Trace Pathways |
Physiology & Pharmacology |
|
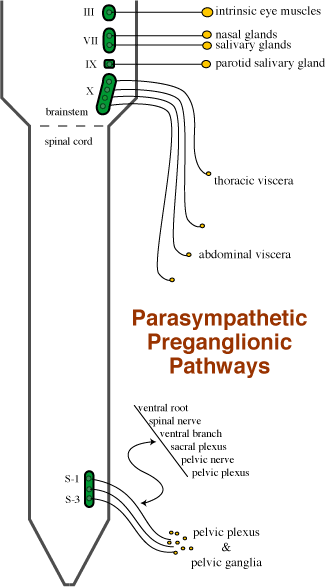
The parasympathetic division of the ANS originates (bilaterally) from the brainstem and from sacral segments of the spinal cord. Preganglionic neurons synapse in discrete autonomic ganglia except in the case of the vagus nerve. Preganglionic axons in the vagus nerve synapse on terminal ganglia located within plexuses inside the visceral organ being innervated. A microscope is required to view terminal ganglia.
|
|
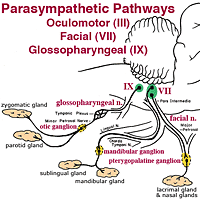
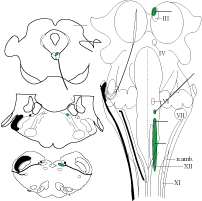
Brainstem Images (click to view enlarged) Left. Parasympathetic pathways are illustrated for three cranial nerves that innervate viscera located in the head. The oculomotor nerve innervates smooth muscle within the eye. Facial and glossopharyngeal nerves innervate glands. Right. Brainstem locations of parasympathetic nuclei are shown from three proints of view (dorsal, sagittal, and transverse). |
 |
 |
