| Home Page |
General ANS Features |
Sympathetic Division |
Parasympathetic Division |
Trace Pathways |
Physiology & Pharmacology |
Visceral efferent (VE) pathways that innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands involve two neurons and a synapse within an autonomic ganglion. The cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons are in the brainstem or spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). The cell bodies of the postganglionic neurons are in autonomic ganglia located peripherally. Axon terminal of preganglionic neurons synapse on dendrites and cell bodies of postganglionic neurons. (In contrast, somatic efferent (SE) innervation of skeletal muscle involves only a single neuron; its cell body in the CNS.)
The advantage of two neurons is conservation of space in the CNS, by shifting neurons into the spacious periphery. The small number of CNS neurons utilize divergent circuits to drive the numerous peripheral neurons. (This strategy has succeeded, in just gut wall alone there are more neurons than in the entire spinal cord.) The disadvantage of moving neurons out of the CNS is reduced brain control, but decreased brain control is not a problem in the case of visceral organs which have a limited repertoire of actions.
Preganglionic axons are myelinated, which means that they conduct more rapidly than do the numerous non-myelinated postganglionic axons. However, non-myelinated axons are metabolically more efficient and reduced conduction speed is not a problem in cases of smooth muscle contraction and gland secretion.
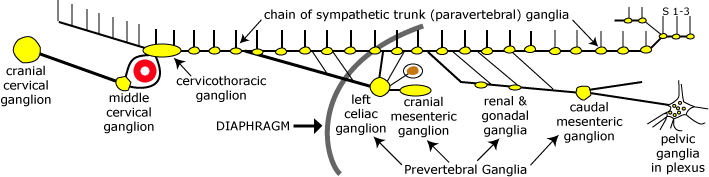
The following image shows postganglionic neurons within an autonomic ganglion. The neurons exhibit pale eccentric nuclei that contain a prominent nucleolus. Embryologically, postganglionic neurons arise from neural crest and migrate to populate autonomic ganglia.
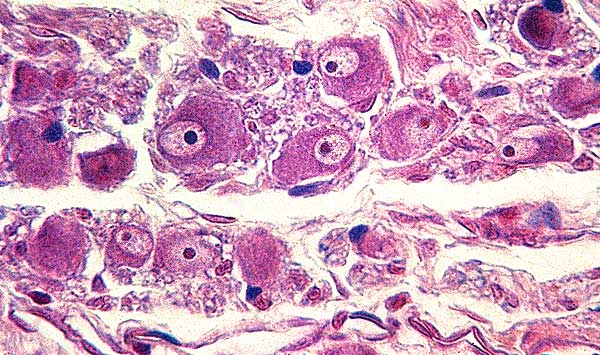
The following schematic image shows locations of a number of autonomic ganglia (yellow ovals) in the periphery. A bilateral chain of paravertebral ganglia is located beside vertebral bodies in thoracic and abdominal cavities. Prevertebral ganglia are located around major vessels within the abdomen. Cervical ganglia are located in the vicinity of the neck.